Clinical trials are a crucial component of developing new treatments and therapies. They have the potential to shed light on the safety and efficacy of medical innovations. However, as with any type of market research in pharma, they present a number of ethical challenges that must be addressed in order to ensure the highest possible standards of safety and ethical rigor are met.
In this blog, we will explore the key ethical considerations that arise in clinical trials and discuss how healthcare providers and researchers can balance ethical concerns with the desire for innovation. We will discuss some of the common ethical challenges in clinical trials, including issues related to informed consent, participant selection, and conflicts of interest.
At ZoomRx, we believe that healthcare providers can play an important role in promoting ethical clinical trial practices. HCPs can help to ensure that clinical trials are conducted with the highest possible ethical standards by remaining vigilant for potential risks to patient safety, ensuring that patients are fully informed about the risks and benefits of participation, and advocating for appropriate patient selection criteria.
Ethical Considerations in clinical trials
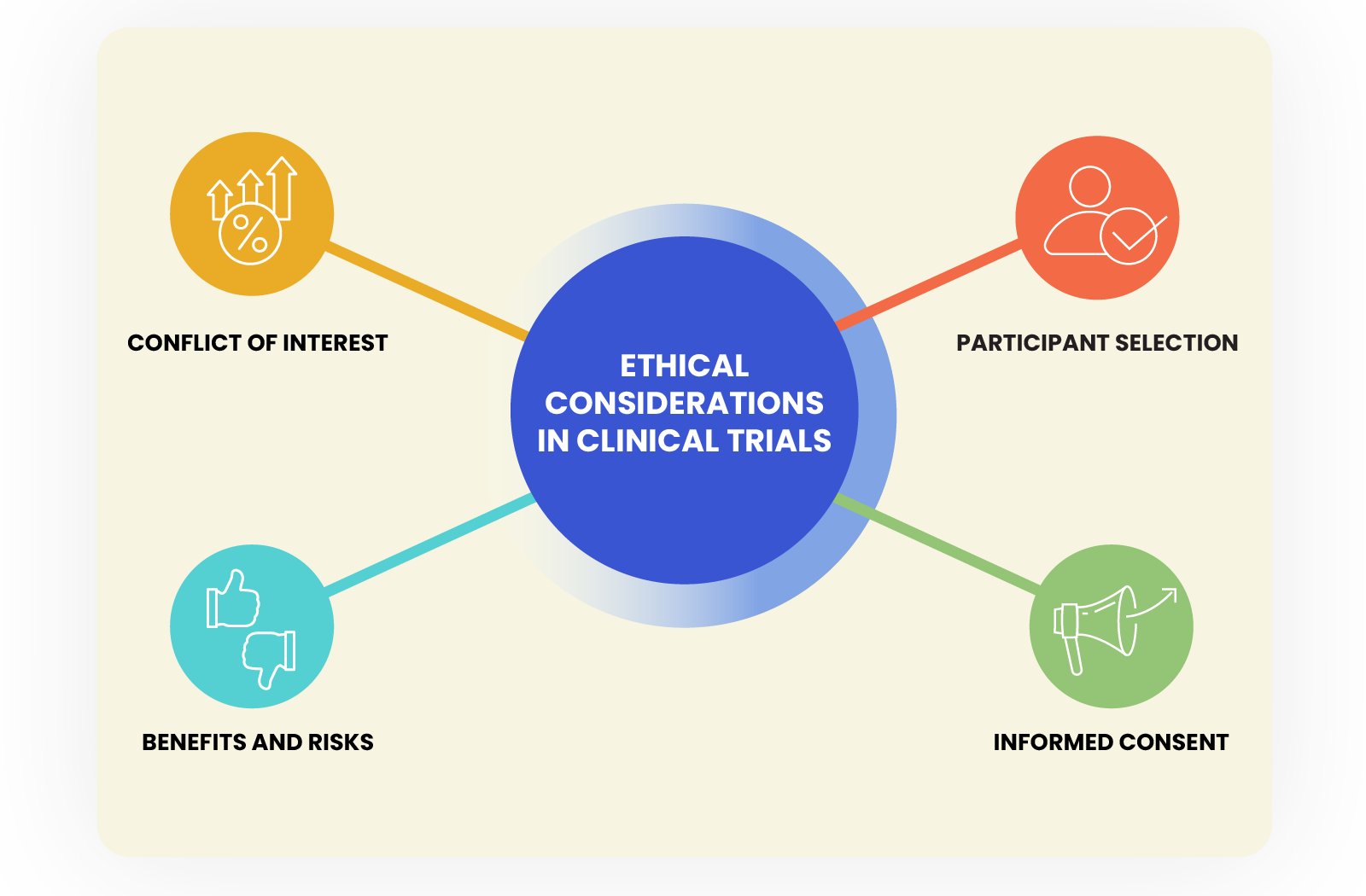
Clinical trials have the potential to save lives and improve patient outcomes, but they also raise a range of ethical concerns that must be carefully considered and addressed. Some of the key ethical considerations in clinical trials include:
Informed consent: Informed consent is a cornerstone of ethical clinical research. Participants must be fully informed about the risks and benefits of the trial, as well as the potential alternatives, before they can make an informed decision about whether to participate. This includes ensuring that participants understand the nature of the research, the risks and benefits, and their right to withdraw at any time.
For instance, the Tuskegee Syphilis Study was conducted by the U.S. Public Health Service in the 1960s has enrolled 600 African American men, 399 of whom had syphilis, and withheld treatment from them even after a cure was discovered. The men were not informed of the true nature of the study and were instead told that they were receiving free medical care. This study violated the principles of informed consent, as the participants were not given the information necessary to make an informed decision about their participation.
Participant selection: The selection of participants in a clinical trial must be fair and based on clear criteria. Flaws in the participant selection process can have devastating consequences, and pharmaceutical companies must take all necessary precautions to prevent such occurrences. The proper implementation of participant selection and safety protocols is essential to maintaining the integrity of clinical trials and protecting the well-being of participants.
For instance, In 2016, a clinical trial for a new cancer drug was launched by pharmaceutical company Bial in France. The trial was conducted on 90 healthy volunteers and aimed to test the safety and tolerability of the drug. However, during the trial, one participant died and five others were hospitalized with neurological symptoms.
The cause of the adverse events was traced back to a flaw in the participant selection process. The trial included volunteers who were not eligible for the study due to pre-existing health conditions, and the dosages given to participants were higher than those recommended in previous animal studies.
This trial raised concerns about the importance of appropriate participant selection and safety protocols in clinical trials. Bial was criticized for failing to adequately screen participants and for not following proper dosage guidelines. The company was fined €195,000 and the trial was suspended.
Conflict of interest: Conflicts of interest can arise in clinical trials when researchers or other parties involved in the trial have financial or other personal interests that may influence the study results.
One such instance In 2018, Novartis, a pharmaceutical company, was criticized for its involvement in a clinical trial of a gene therapy for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a rare and often fatal genetic disease. Novartis was accused of manipulating the trial data to make the therapy appear more effective than it actually was.
The trial was designed as a randomized, double-blind study, meaning that neither the researchers nor the participants knew whether they were receiving the gene therapy or a placebo. However, after the trial ended, it was revealed that Novartis had unblinded some of the data, giving the company an advantage in interpreting the results.
Novartis was also criticized for the high cost of the therapy, which was priced at $2.1 million per treatment. Critics argued that the high cost made the therapy inaccessible to many patients and raised questions about Novartis' motives in conducting the trial.
Benefits and Risks: Clinical trials are designed to test the safety and efficacy of new treatments, but they also involve risks for the participants. HCPs and researchers must ensure that the potential benefits of the study outweigh the potential risks, and that the risks are minimized as much as possible.
For instance, In 2006, a clinical trial of the pain medication TGN1412 was conducted in the UK. The study was designed to test the safety of the drug in healthy volunteers, but within minutes of receiving the drug, the participants experienced severe adverse reactions, including organ failure and life-threatening blood clotting. The study raised questions about the potential risks of early-phase clinical trials and the need to balance the potential benefits of new treatments with the risks to study participants.
By carefully considering and addressing these ethical considerations, healthcare providers and researchers can ensure that clinical trials are conducted with the highest possible standards of safety, scientific rigor, and ethical conduct.
Best practices for ethical conduct in clinical trials

To promote ethical conduct in clinical trials, healthcare providers and researchers should follow best practices that prioritize patient safety, transparency, and scientific rigor. Some of the key best practices include:
Developing a clear protocol: A well-designed protocol ensures that the trial is conducted safely, ethically, and with scientific rigor.
Protecting participant safety: Participant safety should be the top priority in clinical trials. Healthcare providers and researchers should carefully monitor participants for adverse events and take steps to mitigate any risks.
Ensuring data integrity: Researchers should use validated methods for collecting and analyzing data, and ensure that the data is accurate, complete, and unbiased.
Maintaining confidentiality: Researchers should ensure that participants' personal information is kept confidential and that any data shared is de-identified to protect participant privacy.
By following these best practices, healthcare providers and researchers can help ensure that clinical trials are conducted with the highest possible standards of safety, scientific rigor, and ethical conduct.
Conclusion
In conclusion, clinical trials are an essential tool for developing new medical treatments and therapies. However, they present a range of ethical considerations that must be carefully considered and addressed to ensure the highest possible standards of safety and ethical rigor. By following best practices and promoting ethical conduct, healthcare providers and researchers can help to ensure that clinical trials are conducted with the highest possible standards of safety, scientific rigor, and ethical conduct.